Occupational Safety and Work Environment
Security Management System for Occupational Health and Organizational Environment
PTG establishes an industrial product standard system, which will integrate three systems together (Integrated Management System), referred to as “management system” according to TIS 9001-2559, ISO 9001: 2015 Quality Management Systems Requirement TIS 14001-2515, ISO 14001: 2015: Environmental Management System Requirements, and TIS 45001-2518, ISO 45001: 2018 Occupational Health and Safety Management System.
In managing occupational health and safety within the organization, the Company has established the Quality, Security, Occupational Health and Safety, Environmental Policy (QSSHE) to oversee and control the operational processes, continuous productivity improvement to make operators aware of operations to address risks and opportunities in QSSHE of the organization and all groups of stakeholders.
In addition to using international standards in the management of security, safety, occupational health, and the environment to ensure that all business units will adopt security, safety, occupational health and the environment standards as part of business operations, the Company has established a system of standards for security, safety, occupational health and the environment of PTG Group (PTG SSHEMS) with the objective of overseeing management standards for security, safety, occupational health and the environment to ensure consistency throughout the organization. The goal of the PTG SSHEMS system aims to achieve
ㆍZero Accident
ㆍZero Environmental Claim
ㆍZero Security Incident
ㆍZero Process Safety Event
The system has been implemented through the wheel of PDCA, consisting of 14 requirements, each of which consists of 4 dimensions:
ㆍContent :
Establish written operating procedures.
ㆍDeployment :
Effectively communicate operational procedures to operators.
ㆍConformant :
Follow the manual and procedures correctly.
ㆍPerformance :
The effectiveness of the operation.
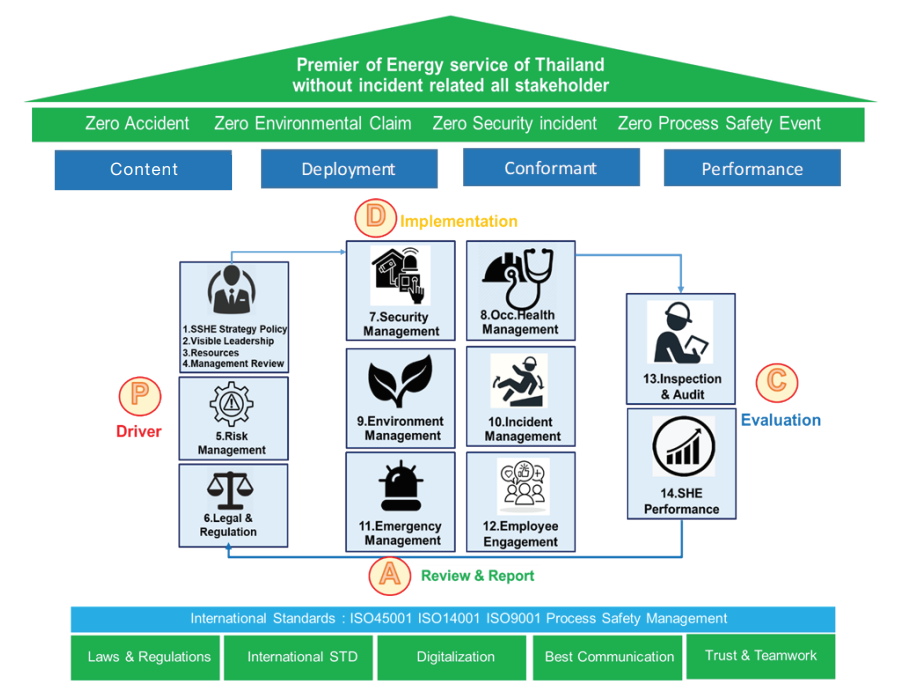
Safety Management Structure for Occupational Health and Organizational Environment
1) Group level: PTG has established a committee to oversee security, safety, occupational health and environmental policies. The Chief Executive Officer and the President act as the chairman, with the managing director from its subsidiaries serving as committee members. The Department of Safety and Environment shall act as the secretary to perform duties and responsibilities to determine the direction of security, safety, occupational health and environment management within the Group.
2) Business group level: PTG has included security, safety, occupational health and environment agendas as part of its monthly operations meeting so that the relevant middle management team can participate in the safety work promotion activities and be a leader in activities that promote safety in the area.
3) Operational area level: PTG has arranged for every operating area to have a safety committee of its own to be in accordance with applicable laws. The committee is responsible for managing security, safety, occupational health and environment in the area to follow up on suggestions from employees as well as the progress of safety issues. The committee is also responsible for planning and leading safety promotion activities.
Safety, Health and Environmental Risk Assessment
PTG identified hazard indicators, addressing environmental risks, assessing ESG risks and opportunities related to its operations, the production of products and services, and taking into account life cycle, changes or modifications to activities in normal and abnormal conditions, including emergencies, as follows:
● Hazard identification
The Company has in place a process to identify hazards in the management system. In this process, the Company considered work instructions, social factors, negative factors from being a consultant, leadership and corporate culture, routine or non-routine activities and situations, including dangers arising from infrastructure, materials, equipment, etc. The Department of Safety and Environment has applied the hazard identification results and improve management of safety and occupational health. In the process of risk assessment, there is an assessment covering security, safety, occupational health and environment in every process of the operation.
● Reporting on work-related hazards and safety
The company has organized a health risk assessment process. Through this process, the company has considered various risk factors that employees are exposed to. duration of exposure and current preventive measures Including setting up a plan for employee health examinations. Both in the case of entering new work, changes in work that affect risk factors that are different from before, annual health examinations and perform health checks according to the nature of work with other specific risks, such as confined space work, driving work transporting hazardous materials, etc., to ensure that employees are in good health. Suitable for the working environment and in cases where it is found that there is a health risk Control measures have been considered. and immediate measures to reduce risk before the employee or those involved will be affected by their health from their work.
● Reporting on work-related hazards and safety
PTG laid out a system for reporting security, safety, occupational health and environmental issues, which is divided into the following types.
1. Work accident and incident report: When an accident occurs, employees must immediately report to their supervisors and safety officers working in the area through the specified channels. Then, it must enter the process of investigating the root cause based on the Company’s process through a meeting of the Safety Committee in order to prevent and correct and ensure that it shall not recur.
2. Unsafe act and working environment Report: When employees encounter unsafe working conditions, they can report through Safety PT Service for further analysis and corrective action, and follow-up through the meeting of the Area Safety Committee.
3. Non-compliance report from internal audit: PTG has arranged an internal audit on the SSHE based on its safety, occupational health, and environmental management system and international standards. System assessment is conducted at least once a year and there is also a monitoring and correcting process by issuing a non-conformity report.
PTG formulated a policy to provide employees with the right to stop working when they find out that the work area is not safe (Stop Work Authority). This policy is part of the safety culture "Stop if Unsafe,” which has been promoted within oil and gas depot operations and transportation. The culture is shaped up as the executives place importance on and are committed to complying with the Stop Work Authority policy by acting as a role model in accordance with the “Visible Leadership” requirement. As for part of employees and contractors, they need to stop working immediately and raise their concern to their supervisor when they feel unsafe. In this regard, the Company also provides rewards for employees who perform admirably (Safety Bonus) and penalties are imposed for those who violate the safety rules.
PTG has established a process for reporting and investigating the causes of accidents and incidents in operation. According to the requirements of ISO 45001:2018, the investigation process is conducted by a committee with specific expertise using international interrogation tools that allow to find the true cause of the incident. This is conducted with a focus on systematic solutions. After the investigation ends, a professional safety officer in charge will be responsible for following up on remedial issues from the investigation and review the risk assessment results in all aspects to prevent the incident from occurring at other areas.
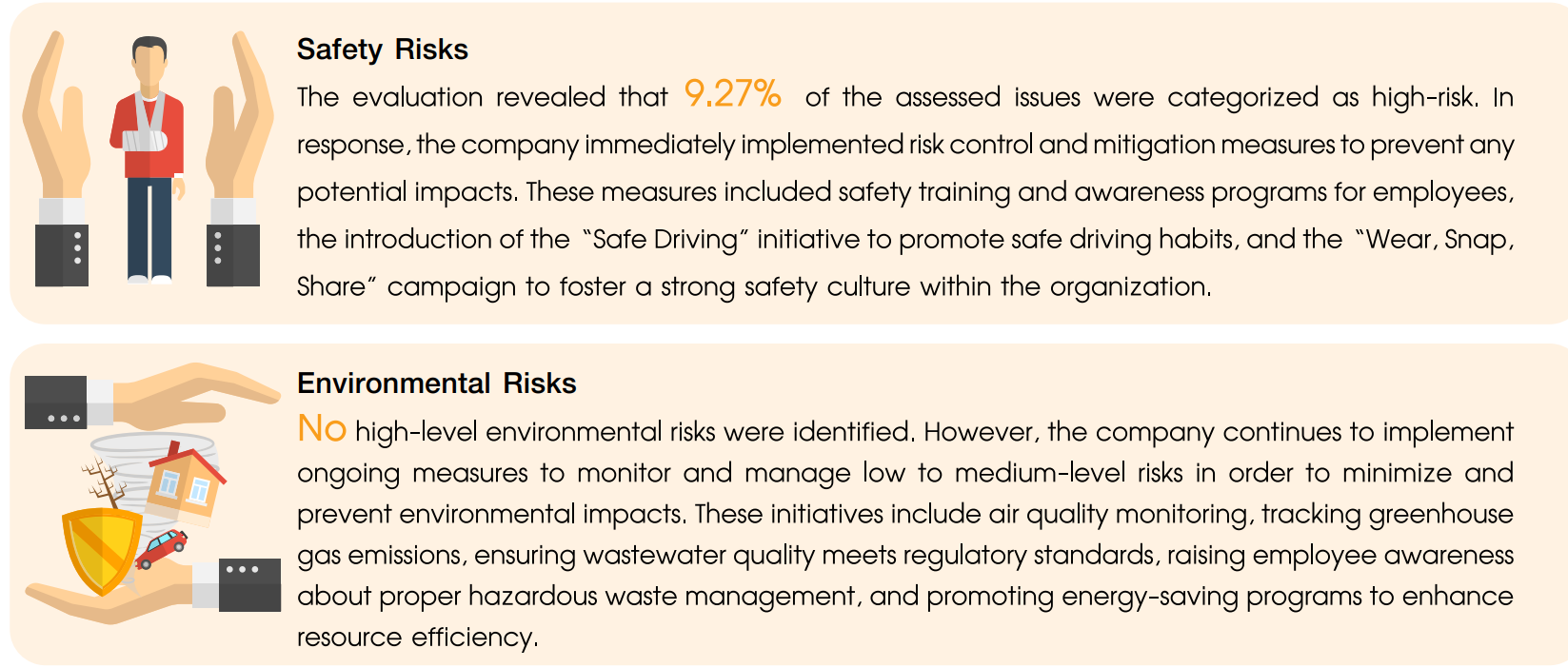
Outcomes of the 2024 Risk Assessment
PTG is committed to continuously assessing and reviewing occupational health, safety, and environmental risks across all activities and areas. The company places significant importance on regularly reviewing risk control and mitigation measures, at least once a year, to ensure safe operations that align with established standards. In 2024, the company conducted a risk assessment focused on two key areas: safety risks and environmental risks. The assessment results were as follows:
Emergency Preparedness and Response
The company recognizes the importance of workplace safety and has established a comprehensive emergency management system covering prevention, response, and post-incident recovery. The details are as follows:
1. Risk Assessment and Prioritization The company reviews relevant laws, standards, and requirements on safety, occupational health, and environment. It also analyzes historical accident and emergency statistics, as well as risk assessment results for each area, to prioritize actions and update emergency plans appropriately.
2. Emergency Plan Development Emergency plans are prepared for each area, covering prevention measures, response, evacuation, relief, first aid, and recovery. The plans define the severity levels of incidents to provide appropriate procedures, whether managed internally or with external support.
3. Resources and Personnel Preparation The company assigns roles and responsibilities for personnel involved in each plan, considering their skills and expertise. Safety equipment, personal protective equipment (PPE), and alarm systems are provided and regularly checked for readiness.
4. Communication and Training Training is provided to all employees and contractors to ensure they understand their roles, reporting procedures, and emergency response steps. Safety information such as SDS (Safety Data Sheets), PPE usage instructions, and safe working procedures are disseminated. Communication is also extended to surrounding communities and relevant stakeholders as appropriate.
5. Drills and System Testing Emergency drills are conducted at least once a year, at both departmental and organizational levels. Government authorities, local agencies, and external units such as fire departments are invited to participate to enhance cooperation and preparedness. Post-drill evaluations identify challenges and suggestions to improve plans and procedures.
6. Continuous Review and Improvement Emergency plans are reviewed at least annually or after actual incidents, based on drill results, external feedback, and legal requirements. Reports summarizing drill outcomes and review results are prepared for management and submitted to relevant authorities as required by law.
Operations to improve the quality of OSHE
PTG establishes a committee to oversee security, safety, occupational health and environment policies to determine and align the direction of security, safety, occupational health and environment management within the Group. This committee consists of Chief Executive Officer and President being the Chairman. There are managing directors from subsidiaries serving as committee members and has the Safety and Environment Department as the secretary of the operation.
PTG established the Department of Safety and Environment to take care of the management of work safety in the workplace and develop the performance of occupational health and environment in accordance with the law and international standards to reduce potential impacts on stakeholders due to business operations in the development of safety, occupational health and environment systems. The Company complies with and obtains certification according to international standards ISO14001 : 2015 & ISO45001 : 2018 in the scope of processing, receiving, storing and distributing fuel products within the oil terminal in order to be a model for improving the management system and developing personnel at the same time. In the near future, the scope will be expanded to cover all processes and oil terminals.
The Department of Safety and Environment strives to enhance the organization's potential in terms of safety in all business activities throughout the supply chain by initiating and improving work processes to ensure continued efficiency and safety in order to transform PTG into an organization of excellence as follows:
- Management of Security, Safety, Occupational Health and Environment at Oil Depots
The Department of Safety and Environment focuses on developing security, safety, occupational health and environment management systems to comply with laws and international standards. The oil depots have developed the security, safety, occupational health and environment management systems of PTG Group (PTG SSHEMS) according to international standards (ISO 45001: 2018), which are used as a guideline and framework for project implementation within oil depots.
PTG opens up opportunities for employees to be part of building up safety promotion activities within oil depots. For example, a project to improve work area with ergonomic assessment (Mae Klong Oil Depot), a warehouse improvement project using 5S principles (Khon Kaen Oil Depot), both of which received a national Kaizen Award. Moreover, at every oil depot, there will be safety officers assigned to monitor work area. The qualifications of this position as required by law are: 1) Safety officers of the executive level (all executives); 2) Safety officers of the supervisory level (all supervisors); 3) Professional safety officers at oil depots. Every depot has an Occupational Safety Committee that represents employees to manage security, safety, occupational health and environment in the area, as well as planning activities to promote safety within oil depots under PTG SSHEMS.
Every depot has plans in place to respond to emergencies and crises to ensure that the situation can be addressed accurately and in a rapid manner in order to reduce potential loss caused to the depot, the community and the surrounding environment. For every plan, there will be at least one rehearsal per year and it will be improved and developed to be in line with changes occurring, both inside and outside the oil depots.
- Safety inspection and training in service stations
Department of Safety and Environment is aware of the safety of all visiting customers at PT service stations, thus conducting internal safety audits that cover all businesses in service stations to identify risks and potential causes of various dangers, which will cause an impact on safety and occupational health of employees and visiting customers, or may cause damage to the property of the company and that of customers. Incidents can happen at every part of the service station, be it at the dispensing yard or fuel dispenser. The Department of Safety and Environment shall work further on the obtained hazard information for correction, improvement and identification of preventive measures before an accident or incident occurs in the service station, as well as reporting to the Safety and Environment Committee and follow up on corrective actions until they are completed. In this regard, high and very high risk issues shall be reported to the management for acknowledgment and urgent action taken under the Enterprise Risk Management Committee.
In the preparation of audit reports and the monitoring of safety and environmental issues in service stations, the Department of Safety and Environment has employed Power BI to provide in-depth analysis of business data. The data can be managed through the dashboard in real time, with the system being able to work flexibly with the Safety PT Service. It can also reduce work time of employees, including use of paper by 100 percent, and being able to set access rights for users, making it highly secure in data usage.
In addition,
the Department of Safety and Environment has raised awareness and participation of employees in safety management through safety promotion activities such as Safety Clinic that will educate and raise awareness among employees of service stations to ensure that they can work with well-being and contentedness.
- Management of security, safety, occupational health and environment, transportation, safety inspection and training for oil transporting drivers
The Department of Safety and Environment realized how important transporting PT gasoline fresh daily is, thus it assigned safety officers to work in the transportation business, planning and developing a SSHEMS plan to be applied to the transportation of the Company's products under the management framework of the PTG SSHEMS.
PTG has directed its subsidiary PTG Logistics Co., Ltd. to carry out activities related to security, safety, occupational health, and environment management in consistent with the Group’s requirements. It formulated a SSHEMS policy and established a safety committee to work in each specific area to shape and plan the SSHEMS to ensure that accidents arising from product transportation can be prevented.
PTG has set up a safety driving training center for delivery drivers to ensure that the number of accidents and impacts on stakeholders as a whole can be limited to zero under a project called "PTG Gentleman: Disciplined, Generous, Unselfish," which aims to raise awareness of safe driving among driver employees. In addition, PTG has used an AI system to detect driver abnormalities, which helps to make sure that the drivers are ready to work, along with random screening for drugs and alcohol. There is a policy to prevent the use of drugs and marijuana within the Company by considering the suitability and safety of drivers based on criteria specified in government policies.
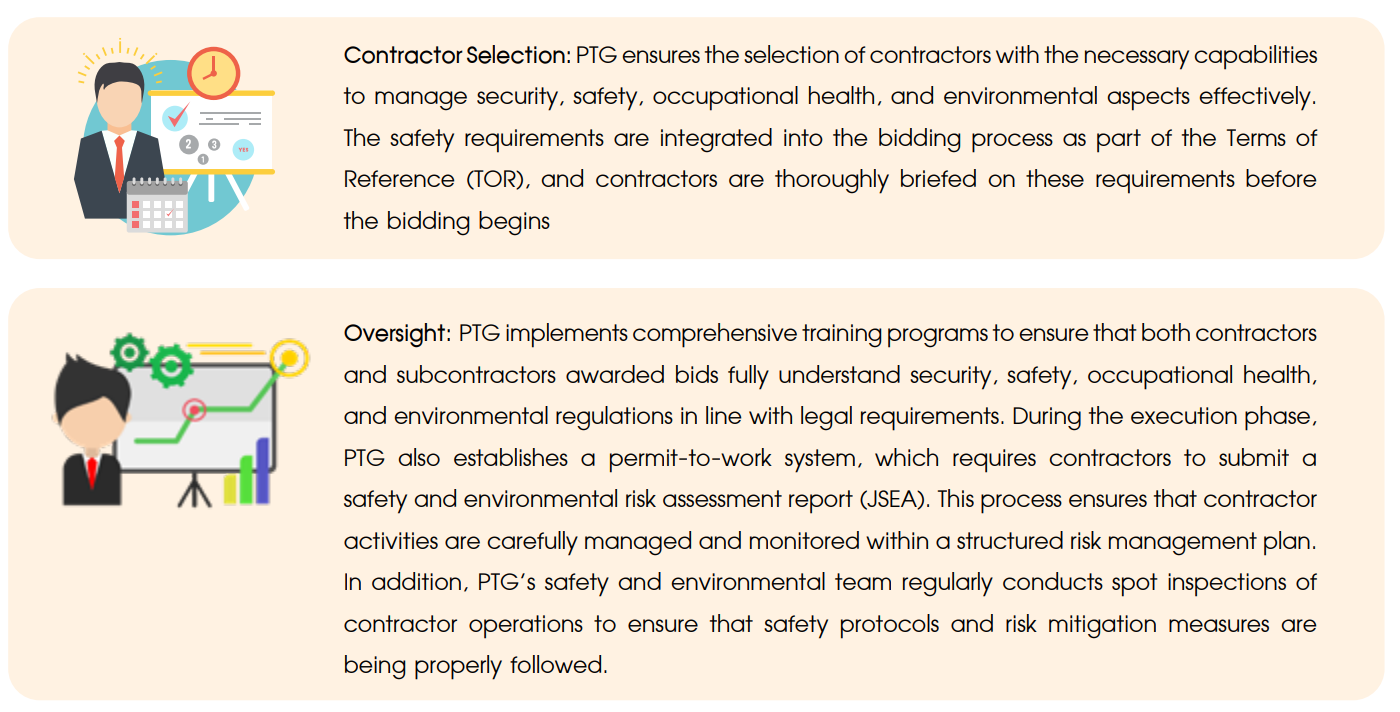
- Promotion of safety for contractors
- Communication of safety requirements in the selection of commercial service station contractors (Model A).
The Department of Safety and Environment set up a unit that supervises the security, safety, occupational health and environment of contractors. In the process of controlling and supervising contractors’ safety, the following actions must be taken:
- Preparing and communicating safety regulations to contractors
The Department of Safety and Environment has developed a work safety manual to control operations at risks for all construction contractors. The manual is used as a guideline for operations concerning safety and working environment, which can be correctly and completely implemented as required by law, including contractor accident reporting. This manual is applied to all construction contractors at LPG gas stations, Max Mart convenience stores, PunThai coffee, Coffee World, Autobac, PTG Logistics Co., Ltd., Max Camp service points, and oil and liquefied petroleum gas transportation companies.
Performance Results in 2024

- Prevention of business impacts and hazards on communities
The Department of Safety and Occupational Health always hold a public hearing to open for opinions of stakeholders, which include communities located close to new service stations and LPG stations to be launched. Steps can be as follows:
- Prepare information and control the construction to ensure safety during the construction. A clear demarcation of the construction area and personal protective equipment (PPE) shall be ensured with safety officers to work onsite. Work safety of the contractors shall be inspected. In the event that a contractor is required to work in high risk, a contingency plan must be submitted and fire extinguishers must be prepared at different points within the work area where there might be materials that can cause sparks to preliminarily cease the incident.
Occupational Safety Goals
| INDICATORS | PERFORMANCE | GOALS | |||
| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2027 | |
| Total Recordable Injuries Rate (TRIR) per one million hours worked by employees* | 0.71 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.315 |
| Number of employees/contractors died while working (persons) | employee 1 contractor 0 |
employee 1 contractor 0 |
employee 0 contractor 0 |
0 | 0 |
| Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR) per million hours worked of employees and contractors | employee 0.69 contractor 0.8 |
employee 0.69 contractor 0.54 |
employee 0.605 contractor 0.45 |
employee 0.552 contractor 0 |
employee 0.276 contractor 0 |
| Occupational Illness Frequency Rate (OIFR) per one million hours worked by employees | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Note:
- Work-related death information Frequency rate of work injuries resulting in time lost from work and the frequency rate of occupational illnesses covering the PTG Energy Group of companies.
- Total work injury rate Covers the operating locations of PTG, MSS, MAX, PTGGE, PTGLG, ATL, PTC, OLP, MaxMart, PUN, SAB, oil depots, distribution centers.
Download Occupational Health and Safety Commitment
Preventive measures to control accidents and work-related illnesses
The PTG Energy Group has expanded its business, resulting in new businesses and a continuous increase in the number of employees within the organization. However, to ensure the safety of employees, contractors, as well as to prevent any adverse impacts on stakeholders such as communities and other parties, the company has established preventive measures to control accidents and work-related illnesses within the PTG Energy Group as follows:
1. Studying standard operating procedures regarding security, safety, occupational health, and environmental matters, and planning compliance with relevant laws, contracts, and international standards.
2. Implementing standard systems for security, safety, occupational health, and the environment within the organization, such as ISO9001:2015, ISO14001:2015, ISO39001, ISO45001:2018, Process Safety Management (PSM), and PTG SSHEMS.
3. Establishing quality policies for security, safety, occupational health, and the environment within the PTG Energy Group to guide continuous improvement efforts.
4. Setting safety and environmental objectives within the Group through various key performance indicators, PTG Energy Group also conducts continuous monitoring and annual assessments of health and safety performance. These results are benchmarked against industry peers to inform the development and enhancement of effective safety measures across service stations and other units, including improvements in areas such as:
a. The rate of injuries requiring hospital treatment or more (TRIR) times per 200,000 hours decreased by 40% (TRIR target ≤0.126): Performance in 2023, TRIR value = 0.171, which indicates that the incidence rate Accidents of the company group Not according to goal But compared to the base year (TRIR 2021 = 0.21), it was found to have decreased by 18.57%
b. Safety Management System assessment according to PTG SSHEMS Score requirements, target ≥2.5 points in all business groups. The performance in 2023, the assessed score = 2.6, is in line with the target
c. Safety sustainability certification. and environmental aspects of the PTG Energy group of companies that have been certified by external agencies. Target ≥ 8 certifications. The performance in 2023 includes a total of 17 certifications received by the PTG Energy group of companies. Certifications such as outstanding safety establishments, green offices, drug problem prevention and resolution, greenhouse gas emissions reduction certification (LESS) meet the goals.
5. Establishing a Safety and Environment Department to oversee safety, occupational health, and environmental conditions within the organization.
6. Forming Safety Committees in each company within the group to facilitate communication between management and employees in addressing safety, occupational health, and environmental concerns.
7. Providing training on safety, occupational health, and environmental laws and regulations, including basic safety, fire safety, safety management for managers, and various operational safety courses.
8. Developing leadership skills in safety management among executives and supervisors to ensure informed decision-making and confidence-building among subordinates.
9. Developing safety, occupational health, and environmental regulations and manuals for each business unit within the group.
10. Conducting joint accident investigations with relevant parties to identify root causes and implement corrective/preventive measures to prevent recurrence and extend lessons learned to related areas and business units within the organization.
11. Summarizing accident statistics and analyzing safety, occupational health, and environmental data within the organization to identify trends and develop strategies for risk management related to workplace injuries/illnesses, safety, environment, and process safety.
12. Studying external incidents to analyze internal risks within the organization and develop preventive measures for serious accidents within the organization.
13. Conducting workplace and equipment inspections for safety, occupational health, and environmental concerns using various methods to identify risks and take immediate corrective actions.
14. Organizing safety promotion activities involving employee participation to enhance awareness and skills related to security, safety, occupational health, and the environment.






